Hair Today, Gone Tomorrow: How Stress Triggers Hair Loss
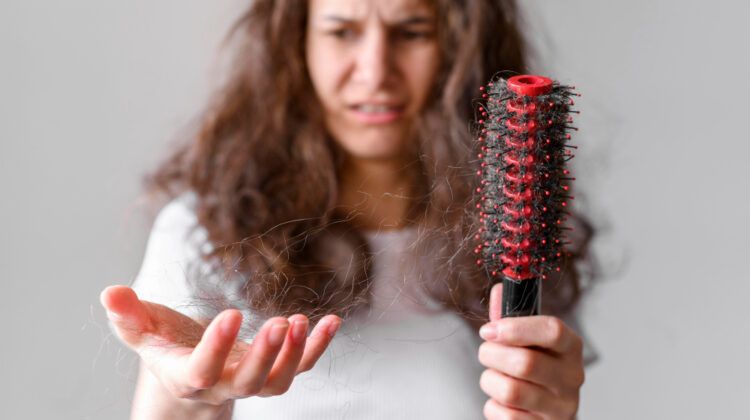

Hair loss is a common concern that affects millions of people worldwide, and its causes are varied and complex. One factor that has gained increasing attention in recent years is the relationship between stress and hair loss. This article delves into the intricate connection between stress and hair loss, exploring the underlying mechanisms, types of hair loss associated with stress, and effective strategies for prevention and management.
Understanding Stress and Its Causes
Definition of Stress: Stress is a natural response to challenges or demands, often referred to as the body’s “fight or flight” reaction. It involves a complex interplay of physiological and psychological responses aimed at preparing the body to confront or escape perceived threats.
Causes of Stress:
1. Environmental Stressors: These include factors such as noise, pollution, or overcrowding that can contribute to chronic stress.
2. Life Events: Major life changes, such as moving, divorce, or the death of a loved one, can induce significant stress.
3. Work-related Stress: High work demands, job insecurity, or a challenging work environment can lead to chronic stress.
4. Financial Stress: Struggling with financial issues, debt, or economic instability can contribute to elevated stress levels.
5. Relationship Stress: Conflicts within relationships, family issues, or social isolation can be potent sources of stress.
6. Health Issues: Coping with chronic illness, undergoing medical treatments, or managing health concerns can induce stress.
7. Cognitive Stressors: Perfectionism, negative self-talk, and excessive worrying can contribute to ongoing stress.
8. Traumatic Events: Exposure to trauma, such as accidents, natural disasters, or violence, can lead to acute or chronic stress.
Understanding Hair Loss and Its Causes
Definition of Hair Loss: Hair loss, or alopecia, is a condition characterized by the partial or complete loss of hair from areas where it typically grows. It can occur on the scalp or other parts of the body and may be temporary or permanent.
Causes of Hair Loss:
1. Androgenetic Alopecia (Genetic Hair Loss): This is the most common cause of hair loss and is often hereditary. It leads to a gradual reduction in hair volume in both men and women.
2. Telogen Effluvium: A type of temporary hair loss where a significant number of hair follicles enter the resting (telogen) phase simultaneously. Common triggers include stress, illness, or hormonal changes.
3. Alopecia Areata: An autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to sudden, patchy hair loss.
4. Traction Alopecia: Caused by excessive tension on the hair, often due to tight hairstyles or hair treatments. It can result in gradual hair loss.
5. Medical Conditions and Treatments: Certain medical conditions like thyroid disorders, lupus, or diabetes can contribute to hair loss. Additionally, treatments like chemotherapy may lead to temporary hair loss.
6. Hormonal Changes: Hormonal fluctuations during pregnancy, childbirth, menopause, or conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) can contribute to hair loss.
7. Nutritional Deficiencies: Inadequate intake of essential nutrients, such as iron, zinc, or vitamin D, can impact hair health and lead to hair loss.
8. Physical or Emotional Stress: Chronic stress can contribute to hair loss through mechanisms like hormonal imbalances, disrupted hair growth cycles, and increased inflammation.
9. Age-related Hair Thinning: As individuals age, hair may naturally become thinner and finer due to changes in hormone levels and decreased hair follicle activity.
10. Trichotillomania: A psychological disorder where individuals compulsively pull out their hair, leading to noticeable hair loss.
The Interconnection between Stress and Hair Loss
While stress itself is not a direct cause of androgenetic alopecia (genetic hair loss), it can exacerbate or trigger other types of hair loss, such as telogen effluvium, alopecia areata, or trichotillomania. The physiological responses to stress, including hormonal fluctuations, inflammation, and immune system modulation, can disrupt the normal functioning of hair follicles and contribute to hair loss.
Managing Stress and Hair Loss
1. Stress Management Techniques: Incorporate stress-reducing practices such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, yoga, or mindfulness to promote overall well-being.
2. Regular Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity to help manage stress and improve circulation, which benefits both mental and hair health.
3. Balanced Diet: Ensure a nutrient-rich diet with adequate vitamins, minerals, and proteins to support overall health and hair growth.
4. Adequate Sleep: Prioritize quality sleep to allow the body to recover and manage stress effectively.
5. Professional Support: Seek professional help, such as therapy or counseling, to address underlying stressors and develop coping strategies.
6. Medical Consultation: If experiencing significant hair loss, consult with a healthcare professional or dermatologist for a thorough evaluation and personalized treatment plan.
7. Topical Treatments: Consider topical treatments or medications prescribed by a healthcare professional to promote hair regrowth in specific cases.
By understanding the intricate relationship between stress and hair loss, individuals can adopt a holistic approach to managing both aspects of their well-being. It’s essential to address stressors proactively, prioritize self-care, and seek professional guidance when needed to promote not only healthy hair but also overall mental and physical health.
Understanding the Hair Growth Cycle
Before delving into the link between stress and hair loss, it’s essential to understand the hair growth cycle. The human hair growth cycle consists of three main phases:
- Anagen (Growth) Phase: This is the active phase where hair grows continuously for an extended period (2-7 years).
- Catagen (Transitional) Phase: A short transitional phase lasting a few weeks where hair growth slows down, and the hair follicle starts to shrink.
- Telogen (Resting) Phase: The hair follicle is in a resting phase for about 2-4 months before shedding and being replaced by new hair.
Types of Hair Loss Associated with Stress
Telogen Effluvium:
- Overview: Telogen effluvium is a type of temporary hair loss where an increased number of hair follicles shift into the telogen (resting) phase.
- Connection to Stress: Significant stressors, such as illness, surgery, or emotional stress, can disrupt the hair growth cycle, pushing a large number of follicles into the resting phase simultaneously.
- Onset: Hair shedding typically occurs 2-3 months after the stressful event.
Alopecia Areata:
- Overview: Alopecia areata is an autoimmune condition where the immune system attacks hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
- Connection to Stress: While the exact cause is unknown, stress is considered a potential trigger for the onset or exacerbation of alopecia areata.
- Patterns: Hair loss occurs in small, round patches on the scalp, but it can also affect other areas of the body.
Trichotillomania:
- Overview: Trichotillomania is a psychological disorder characterized by the urge to pull out one’s hair.
- Connection to Stress: Stress and anxiety can exacerbate trichotillomania symptoms, leading to increased hair pulling.
- Patterns: Hair loss is often irregular and patchy, depending on the areas where the individual engages in hair pulling.
The Physiology of Stress-Induced Hair Loss
Hormonal Imbalance:
- Cortisol Release: Stress triggers the release of cortisol, known as the “stress hormone,” by the adrenal glands.
- Impact on Hair Growth: Elevated cortisol levels can disrupt the normal functioning of the hair follicles, leading to an imbalance in the hair growth cycle.
Blood Flow Restriction:
- Vasoconstriction: Stress can induce vasoconstriction, reducing blood flow to various parts of the body, including the scalp.
- Nutrient Supply: Inadequate blood flow to the hair follicles can compromise the supply of essential nutrients needed for healthy hair growth.
Inflammation and Immune Response:
- Inflammatory Response: Chronic stress can lead to systemic inflammation, impacting the immune system.
- Immune Attack on Follicles: In conditions like alopecia areata, the immune system mistakenly targets and attacks hair follicles, causing hair loss.
Strategies for Prevention and Management
Stress Reduction Techniques:
- Mindfulness and Meditation: Incorporate mindfulness practices and meditation into your daily routine to manage stress levels effectively.
- Deep Breathing Exercises: Practice deep breathing exercises to activate the body’s relaxation response and reduce cortisol levels.
Regular Exercise:
- Aerobic Activities: Engage in regular aerobic exercises like jogging, swimming, or cycling to boost overall well-being and reduce stress.
- Yoga and Tai Chi: Incorporate activities that combine physical movement with mindfulness, such as yoga or tai chi.
Balanced Diet:
- Nutrient-rich foods: Consume a well-balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and proteins essential for hair health.
- Hydration: Stay adequately hydrated, as dehydration can contribute to stress and affect the hair growth cycle.
Adequate Sleep:
- Quality Sleep: Ensure you get sufficient, restful sleep each night to support overall health and minimize stress.
- Sleep Hygiene Practices: Establish a consistent sleep routine, limit screen time before bedtime, and create a conducive sleep environment.
Professional Support:
- Therapy and Counseling: Seek therapy or counseling to address and manage chronic stressors effectively.
- Medical Consultation: If experiencing significant hair loss, consult a healthcare professional or dermatologist for a thorough evaluation and personalized advice.
Topical Treatments:
- Minoxidil: Over-the-counter minoxidil solutions may help promote hair regrowth for certain types of hair loss.
- Prescription Medications: Consult a healthcare professional for prescription medications that may be suitable for specific conditions.
Conclusion
Stress and hair loss share a complex relationship, and understanding the link is crucial for effective prevention and management. By adopting stress reduction techniques, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking professional support when needed, individuals can mitigate the impact of stress on their hair health. It’s essential to approach hair loss holistically, addressing both the physiological and psychological aspects, to promote overall well-being. Remember, managing stress is not only beneficial for your hair but also for your overall health and quality of life.