How Do You Know if Your Eyes are Infected?
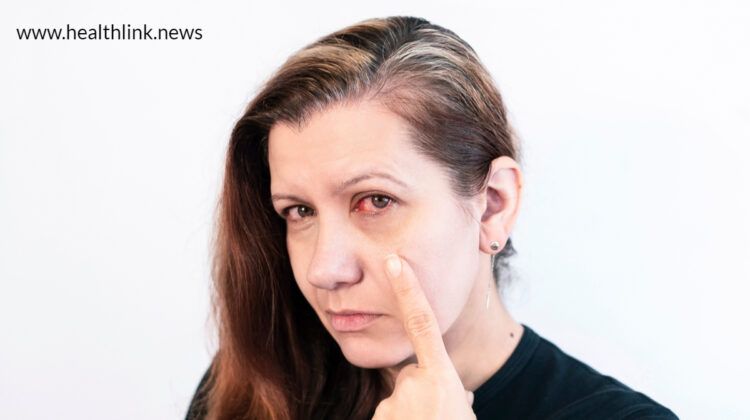

If you are suffering from some pain, swelling, itching, or redness in one or both of your eyes, you have an eye infection. Eye infections fall into three specific categories based on their cause: viral, bacterial, or fungal, and each is treated differently. The good news is that eye infections are not difficult to spot and are easy to treat if caught early enough. This article will help you determine what kind of infection you have, get treatment, and keep it from coming back so you can go on living life full of vision.
1. Keratitis
The cornea is a clear layer that covers your pupil and iris. It helps you see clearly by focusing light rays on the retina. If your cornea gets infected, it can get swollen and red. This is called infectious keratitis. It usually happens if you have a cut or scratch on your eye.
Symptoms of keratitis include:
- Sensitivityto your eyes from light
- Discomfortand pain in eyes
- Swelling and redness in your eye
- Blurry visionand Loss of some vision
- The sensation of having something stuck in your eye
- When you open and close your eyelidsmay cause pain or discomfort.
- Abnormal dischargeand produce tears
You are more likely to develop keratitis if:
- You use contact lenses
- Living in humid and warm place
- Using corticosteroid eye drops for poor eye condition.
- With other illness and conditions your immune is also weak.
- Eyes may get injured by plants with chemicals, which may get into your eyes.
Keratitis is inflammation of the cornea, which is a thin clear layer that forms the front part of the eye. This can occur in the center or near the edge of the cornea. Keratitis symptoms include redness and discomfort when you look at bright lights. Keratitis can sometimes occur because of a viral infection. Keratitis can lead to blurred vision, sensitivity to light, sensitivity to contact lenses, and dry eyes.
2. Blepharitis
Blepharitis is a common eye problem that can range in severity and can cause itching, burning, stinging, and crusting of the eyelids. Clogging of the oil glands inside the eyelid skin at the base of your eyelashes is usually caused by bacteria.
Symptoms of blepharitis include:
- Oil on eyelid
- Sensitive towards light
- Teary eyes more than usual
- Cause burning to your eyes
- Redness, itchiness, swellingto your eyes and eyelids
- Feeling of irritation in your eyes
- Eyelashes crustiness or corners of your eyes
May develop blepharitis:
- Dandruffon scalp or eyebrow
- May have lice on your eyelashes
- Your eye or face may get allergic
- May have oil glands that do not work properly
- Intake of medications that affect your immune system
Blepharitis is an inflammation of the eyelids, specifically their margins. It can be caused by a variety of factors, from certain medications to certain types of bacteria. Treatment for blepharitis will depend on the cause—if it is due to bacteria, your doctor might prescribe oral antibiotics or ointments applied directly to your eyelids. Your doctor might also recommend that you use lubricating eye drops and practice good eye hygiene by washing your eyelids with clean water every day.
3. Conjunctivitis/Pink eye
Infectious conjunctivitis is one of the most common eye infections. The causes of this condition include bacteria, viruses, and various substances that irritate your eyes. Common symptoms of pink eye include redness, swelling, and discharge from your eyes. The severity of symptoms varies depending on whether you are dealing with bacterial or viral conjunctivitis. In some cases, you may also notice a scratchy sensation in your eyes and blurred vision. If left untreated, it could result in serious complications, like corneal ulcers.
It is caused by a virus or bacteria; this type of conjunctivitis is very contagious. Take note of any of the following symptoms and see your optometrist as soon as possible for treatment:
- Tint to your reddish or pinkish eyes
- Thickest watery discharge from your eyes
- Producing more tears in only one eye than usual.
- Itchiness or feeling like there is something constantly in your eyes
Signs and symptoms of eye infections differ depending on the underlying cause. Bacterial conjunctivitis causes crusting, followed by redness and swelling of the outer or inner eyelids. Tears normally drain from the outer edge of your eye, but if you have bacterial conjunctivitis, this drainage may be blocked along with an inflamed, reddened tissue in your tear pathway. Viral conjunctivitis does not cause any crusting of the eye or any discharge but can cause swelling of the eyelids that can temporarily interfere with vision. With allergic conjunctivitis, your eyes will feel itchy, watery, and irritated as a result of allergy-causing irritants like pollen, pet dander, dust, mites, and other allergens.
4. Cellulitis
Eyelid cellulitis is also referred to as periorbital cellulitis, and it can affect your eyelids and the area near your eyes. Some common signs of this condition include eyelid reddening, swelling or puffiness, and excessive crying in young children. For the most part, you will not have any eye pain or discomfort. In fact, with proper treatment and care, most people recover without long-term complications.
Cellulitis is an eye infection that may occur at the back of your eye or the inner corner of your eye. It causes swelling and tenderness. Your eyelids, lashes, and the tissues beneath may become red and irritated. In some cases, you might also notice a watery discharge from your eyes.
Treatment for cellulitis may include:
- Taking oral antibiotics, such as amoxicillin, or iv antibiotics for under 4 children.
- Getting surgery to relieve pressure within your eye if the infection becomes very severe.
- Applying a warm, damp, clean towel to your eye for 20 minutes at a time to relieve inflammation.
5. Ocular herpes
Ocular herpes is a rare but serious form of ocular infection that can be spread by contact with someone who has an active HSV-1 infection. It is not transmitted during sex and is not common. All it takes is just one quick moment when your eyes come in contact with the active infection on someone’s hands, clothing, face, or elsewhere to suddenly find yourself developing eye herpes symptoms.
Symptoms tend to infect one eye at a time, and include:
- Blurvision
- Sensitive from light
- Inflammationof eyelid
- Watery dischargeand thickness
- Corneal tearsor eye tissue
- Irritation of the eyeand pain
Symptoms may go away without treatment after 7 to 10 days or maybe after a few weeks.
Treatment
- Debridement, or brush your cornea with cotton to protect from infection.
- If the infection spreads further into your eye, use Corticosteroid eye drops to relieve inflammation.
- Eye drops and oral medications, or topical ointments, antiviral medication, such as acyclovir (Zovirax).
6. Endophthalmitis
Endophthalmitis can be caused by certain eye injuries, especially injuries to your eye that involve a sharp object. Endophthalmitis can also happen after certain surgeries, such as cataract surgery. Bleeding in your eye is one of the first symptoms of endophthalmitis.
If endophthalmitis occurs as a result of an infection from outside your body, such as from a drop of infected fluid entering your eye, you may experience redness, blurred vision, and tear of the eye. If the infection enters your bloodstream and ends up reaching the eye, it can be very serious and even lead to blindness.
Some symptoms to watch out for, especially after surgery or an eye injury, include:
- Blur vision
- Pus or dischargein your eyes
- Eye painfrom mild to severe
- Sensitive to bright lights
- Vision lossfrom partial to complete
- Around eye and eyelids redness or swelling
Endophthalmitis can cause blurred vision, eye aches and pain, swelling of your eyelids and face, sensitivity to light, and nausea. It is often triggered by surgery or injections into the eye. In some cases, the infection causes permanent blindness. Be familiar with the signs so you can get prompt treatment.
7. Uveitis
Uveitis is a chronic eye disease that happens when your uvea – the central part of your eyeball – gets inflamed from the infection. It can be caused by immune system conditions, viral infections, or injury and often results in inflammation or permanent vision loss if it is not treated.
Uveitis symptoms can include:
- Painin yes
- Blur vision
- Redness in eyes
- Sensitiveto light
- Eye floaters and flashes in your visual field
Uveitis is an intraocular inflammatory disease characterized by a sudden onset of symptoms. It can have systemic implications and due to this, the treatment will vary depending on whether it is the only presenting symptom or if it is associated with other systemic complaints. Treatment for uveitis may include eye drops that open up your pupil to relieve pain, corticosteroid eye drops or oral steroids that relieve inflammation, eye injections to treat symptoms, and/or oral antibiotics for any associated infections. Medications that subdue your immune systems such as anti-TNF agents are used in a small proportion of cases.
Your eye doctor will ask you questions about your symptoms and examine your eyes. It is important to remember that other health conditions can cause similar problems in your eyes — it may not be uveitis. Be sure to mention any other symptoms you are having, such as headache, joint pain, or fever.
8. Sty
Why do I have sties? Sties develop near the glands that are found on the outer edge of your eyelids. These glands can get clogged with dead skin and oils, allowing bacteria to grow. This can cause a sty, which is a pimple-like bump that develops from the gland.
Sty symptoms include:
- Swellingin eyes
- Pain or tendernessaround eyes
- Irritationand itchiness
- Productionof tear
- Crusty eyelids
Frequent sties can be irritating and uncomfortable, but there are several steps that you can take to treat them. Do not try to pop a sty yourself; it can spread the infection or make it worse. Instead, clean your eyelids gently with mild soap and warm water, and ask for an antibiotic ointment that helps to kill the infection. Another treatment is applying a warm cloth to the affected area.
Sty is a minor eye infection that usually goes away with basic home treatment. But you should see your doctor if the pain or swelling gets worse, even with treatment. Sties usually disappear in 7 to 10 days, but it may take longer.