Pregnancy and Diabetes: A Complicated Connection

Pregnancy and Diabetes
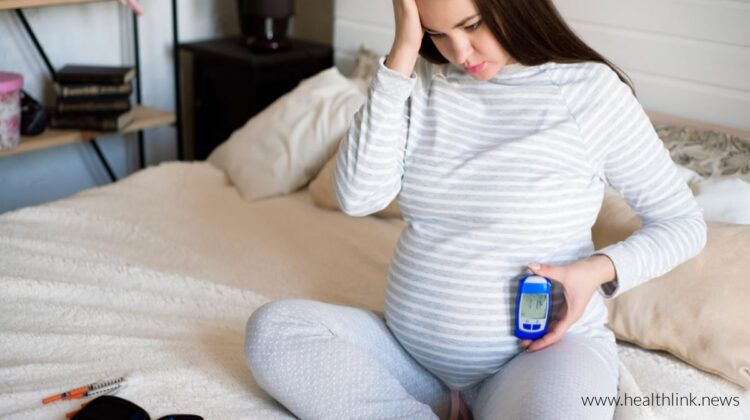
Sometimes women who have diabetes need special health care if they become pregnant. Because the phase of pregnancy is very different and vivid. It requires a lot of nutrition for you and for your baby as well. Therefore, the demand for blood sugar increases during the period of pregnancy. Hence, if you are thinking of getting pregnant and if you do not have diabetes that’s a plus point but if you have diabetes then you need to take care of certain things.
First, you need to get prepared physically and mentally. You need to consult your doctor and check your reports in regards to your diabetic problem and its stats. There are certain tests that you can go for;
- A blood test called glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c, or just A1c)
- Urinalysis test to check the status of your kidney and its problem.
- Cholesterol and triglyceride blood test.
- Eye test to make sure whether you have or not glaucoma, cataract, or retinopathy.
- You can also go for an electrocardiogram.
- Foot exam
- Blood works to make sure your liver and kidneys are working well or not.
These are certain tests that you can go for. Moreover, you need to be cautious and need to give extra care to yourself if you are diabetic and thinking of getting pregnant.
Sometimes people think about how diabetes can affect their baby. Well, babies born to women who are diabetic often have a condition that is known as “Macrosomia.” Macrosomia is a condition in which, when a baby receives high blood sugar from her mother’s blood his or her pancreas starts to make more insulin and thus gets converted to fats, and that is responsible for giving birth to babies weighing more than 9 pounds. Hence, it is always advisable that when you want to have a baby, you need to keep track of your blood sugar level and then follow the prescription given by your doctor.
Gestational diabetes
Gestational diabetes is a problem that happens for the first time during the period of pregnancy (gestation). Gestational diabetes is very similar to other types of diabetes. It affects how your cells use sugar compounds or glucose. Gestational diabetes causes high levels of blood sugar that as a result drastically affect your pregnancy and your baby’s health as well. During pregnancy, some people might develop the problem of gestational diabetes. It is also known as Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). In general, this problem might happen during the 24th or 28th week of the pregnancy.
According to the Centres for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC (Centres for Disease Control)), it is estimated to occur in 2 to 14 percent of pregnancies in the United States.
Gestational diabetes does not imply that you are diabetic before the pregnancy, or will become diabetic after pregnancy. It states that it will increase the risk of having type 2 diabetes in the future. If the right precautions and measures are not taken by the person, it might increase the chances of your child becoming diabetic. And you can also face complications during your pregnancy and delivery.
What type of symptoms can be seen if you have gestational diabetes?
Well, gestational diabetes does not cause any type of symptoms. But sometimes if a person is suffering from gestational diabetes, he or she can face symptoms like;
- Fatigue – fatigue is a term used to describe an overall feeling. The person experiences tiredness, lack of energy, and drowsiness even after having a rest.
- Blurred vision– Blurred vision is a distorted vision in which you cannot see properly.
- Excessive thirst– excessive thirst or feeling dehydrated and it seems as if it cannot be quenched.
- Excessive urination– having the need to go to the toilet very frequently.
- Yeast infection– a yeast infection or fungal infection that causes a lot of irritation and intense itchiness.
Pregnancy and gestational diabetes screening
It is recommended that all women need to get screened during their pregnancy. The screening will allow a wider range of the picture than whether they are suffering from gestational diabetes or not. Screening may be done by taking the woman’s medical history and examining certain risk factors, but an oral glucose tolerance test is also recommended. Now the question comes to what is an oral glucose tolerance test for gestational diabetes? Gestational diabetes as we come to know usually happens during the 24th to 28th week of the pregnancy. The screen test of gestational diabetes makes us understand the problem in the early stages therefore the treatment can be given at the earliest.
The procedure of the oral glucose tolerance test involves quickly drinking a sweetened liquid that needs to contain at least 50g of glucose. The body absorbs this glucose. Because of this, the rise in blood sugar levels increases within 30 to 60 mins. The blood sample will be taken after 60 mins to examine the working process of insulin by the body. The test results that can be observed;
- If the blood glucose level of a person is equal to 140mg/dL or higher it will be identified as gestational diabetes.
- If the value is lowered to 130mg/dL, the identification of the test increases to 90%.
- If your blood glucose level was greater than 130 mg/dL, your provider will recommend you take another diabetes screening test that requires you to fast (not eat anything) before the test.
- During the second screening test (also called a 100-gram oral glucose tolerance test), your blood glucose level will be tested 4 times during a three-hour period after drinking the sweetened drink or any soft drink like cola. If 2 out of 4 results seem abnormal, it is considered that you have gestational diabetes.
What are the causes of gestational diabetes?
It is not certain why some women develop or get gestational diabetes as compared to those who do not get gestational diabetes. The exact reason or factor responsible for getting gestational diabetes is still not known. Moreover, it is considered a hormonal change. So, when you are pregnant, your body develops various hormones and these hormones are produced in bulk. Hormones like;
Human placental lactogen (hPL)
Other hormones increase insulin resistance.
Sometimes, these hormones affect the placenta and help to sustain the pregnancy. What happens is that, as time proceeds, the amount of these hormones increases in your body. This increase of the hormones in the body results in making your body resistant to insulin. Hence, when your body gets resistant to insulin (it is a hormone that is responsible for the regulation of the level of sugar or glucose in the blood), your blood is not able to make a proper regulation with the insulin. During pregnancy, it is normal that your body becomes insulin resistant. This happens because the baby also requires glucose and sugar therefore, your body starts getting resistant to insulin. Moreover, if this resistance becomes too strong, the blood sugar level will rise abnormally and the chances of having gestational diabetes become very high.
Are you at risk of having gestational diabetes?
The person can be at higher risk of getting gestational diabetes if they have;
- If you have high blood pressure.
- If diabetes is in your family history.
- If you are overweight before getting pregnant.
- If you gain a huge amount of weight during your pregnancy.
- If you are expecting multiple babies simultaneously.
- If you have given birth to a baby previously that weighs more than 9 pounds.
- If you had gestational diabetes in previous pregnancies.
- If you had a stillbirth or unexplained miscarriage.
- If you have taken steroids like glucocorticoids.
- If you have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) (it is a situation in which a female hormone level gets affected. In simpler words, women with PCOS produce higher than normal amounts of male hormones.) or any other condition that is concerned with the resistance of the body regarding insulin.
- Being of a certain race or ethnicity, such as Black, Hispanic, American Indian, and Asian American.
If somebody has any one of the above-mentioned problems, then they are at higher risk of getting and developing gestational diabetes.
What will be the complications you can face?
The problem of gestational diabetes, if not carefully managed, can lead to high blood sugar levels. This high blood sugar level can cause serious problems as well. These serious problems might threaten your as well as your baby’s life.
Apart from this, the complications that you and your baby might face are listed below;
- If you have gestational diabetes then the excessive birth weight is a problem that can be seen while being pregnant. If your blood sugar level or glucose level is higher than the standard or normal range. Because of this, overweight babies that weigh more than 9 pounds are more likely to cause injury while giving birth because of their weight.
- Early birth is another problem that can be seen because of high blood sugar levels. Early birth is usually suggested or recommended if the child is more than 9 pounds.
- Your baby might develop respiratory distress syndrome. Respiratory disease syndrome is a condition in which the process of breathing becomes difficult for the newborn.
- Low blood sugar levels can also be seen, sometimes when the baby has a low blood sugar level shortly after birth. In the case of a baby, this results in seizures as well.
- Another problem that can be observed in children is obesity and type 2 diabetes in the later phase of their lives.
- Stillbirth is also prominent if gestational diabetes is left untreated.
- High blood pressure puts your life at risk and the chances of having pre-eclampsia are very prominent. Preeclampsia is a serious complication that can be seen during pregnancy. Because of it both your and your baby’s life are in great danger or threat.
- If somebody has gestational diabetes there is a high chance of having a surgical delivery or a C-section.
- Gestational diabetes is also responsible for having diabetes in future pregnancies as well. In some cases, it can develop into type 2 diabetes as one grows old.
How can you prevent gestational diabetes?
Now the question comes of how you can prevent or treat gestational diabetes? There are certain precautions or measures that you can take to avoid the situation of having gestational diabetes. These are as follows;
Eat healthy foods: maintain a healthy diet and always eat healthy foods. Avoid foods that have ‘fats’ and high calorific values. You can always go for fruits and vegetables to minimize the risk of getting gestational diabetes. You can also consult with a dietitian and stick to a proper diet plan that is provided by your dietitian.
Be active: try to do more exercise. Exercise is important; it reduces the chance of having gestational diabetes before and after pregnancy. You can always start with a small period of exercise time. For example, set a goal for 30 minutes of exercise, do exercise for like 5 days a week, and do brisk walking regularly. This will also help you maintain your shape.
Start pregnancy at a lower weight: if you are planning to get pregnant, getting pregnant at the ideal weight results in a healthier pregnancy. You can cut off those extra pounds and as a result, this will help you to have a healthy pregnancy with minimal chances of having gestational diabetes.
Testing your blood sugar level or glucose level: testing your glucose level is important. This will give you an idea about the situation through which your body is going. Moreover, always try not to get overweight. The concept of gaining weight while going through pregnancy is good but getting overweight is a problem.
Taking medications: if your blood sugar is not stable, then consult your doctors for prescriptions and medications and follow that medication precisely to avoid scenarios that might create problems for you and your baby.
When to consult with a doctor?
If your blood sugar level is not stable then it is recommended to consult with your doctor.
Moreover, you can always go through the entire examination process before getting pregnant so if there is any chance of having gestational diabetes, you will know about it. In cases where you develop gestational diabetes, strictly follow the guidelines as well as the medication that is provided by your doctor and keep good track of your health. Eat healthy food, exercise, and monitor your blood sugar level.