Sex During and After Pregnancy: What You Need to Know?
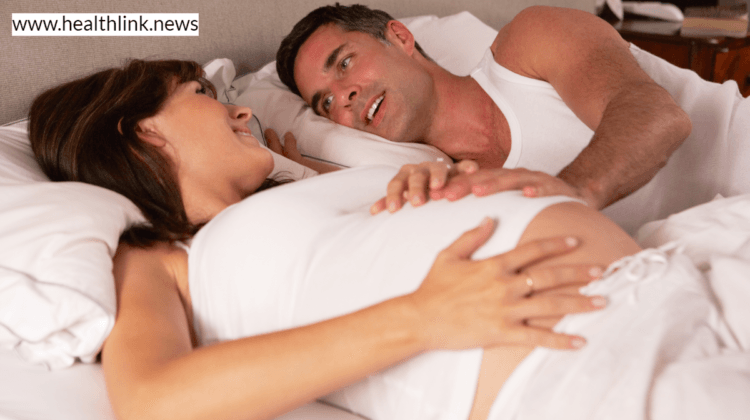

Sex during pregnancy
Sex during pregnancy in simple words means the act of having vaginal, oral, or anal sex while your partner is pregnant. Both pregnant women and their partners often ask their concerns about having sex during pregnancy. If you are pregnant or planning to become pregnant, expect pre-pregnancy sex (i.e., sex to get pregnant) and postpartum sex (expect a less active sex life, if you have a newborn in the house). Can you have Sex During Pregnancy? Is it safe? Can the baby feel it? Is there a time when you should not be doing it? Does sexual desire change during pregnancy? Given the changes and uncertainties that occur during pregnancy, these are all comprehensible questions. The simple answer is that if you have a low-risk pregnancy, it is safe to have sex throughout your pregnancy.
Many women find that in late pregnancy they lose their desire and motivation for sex, not only because of their size but also because they are obsessed with imminent childbirth and the excitement of becoming a new parent.
There are many reasons doctors recommend avoiding sex during pregnancy. These include:
If you have a history of miscarriage or early labour, bleeding from your vagina, leakage of water from the amniotic sac (a fluid-filled sac that holds the baby), sexually transmitted diseases (STDs) that neither partner has treated, vaginal and abdominal pain, the cervix starts to open early, the placenta is covering the cervix opening partially or completely, and if you are pregnant with two or more babies, you are highly recommended to avoid having sex. He will also advise you about having sex if you fit any of these circumstances. Now if you do have sex during pregnancy, you may want to experiment with different positions. When a pregnant partner is lying down, the baby’s weight can put pressure on large blood vessels. This can make the missionary position uncomfortable. Lying during sex helps reduce pressure on the abdomen. You can also try sex with your pregnant partner on top.
Is it okay to have sex while being pregnant?
During all phases of a normal pregnancy, sex is considered safe.
So, you must have thought about what it means to have a normal pregnancy. It is one with a low chance of complications like miscarriage or premature childbirth. If you are unsure whether you fit into this category, talk to your doctor, nurse-midwife, or other prenatal health care professional.
Of course, just because it is okay to have sex when pregnant does not mean you will want to. Many pregnant women notice that their desire for sex alters as the pregnancy progresses. In addition, many women discover that as their bodies become larger, sex becomes uncomfortable.
When it comes to your sexual connection, you and your partner should keep the lines of communication open. Share with each other about ways to meet your intimacy needs, such as kissing, touching, and holding each other. You may also need to try out different sex positions to locate the ones that are most comfortable for you. Many pregnant women lose their desire and enthusiasm for sex late in the pregnancy, not just due to their size, but also because they are obsessed with the impending delivery and the joy of becoming a new parent.
Do you think miscarriages can be caused by sex and or orgasm?
For normal low-risk pregnancies, the answer is no. The contractions that you may feel during and immediately after the orgasm are completely different from labor-related contractions. However, you should check with your doctor to see if pregnancy falls into the low-risk category.
Health care providers also say that as a safety precaution, all women refrain from having sex during the last few weeks of pregnancy, as semen contains chemicals that can stimulate contractions. It is recommended to ask your doctor what you think is best.
It is quite normal for the possibility of libido to increase or decrease during pregnancy. Many pregnant women find that symptoms such as fatigue (very tired), nausea, tenderness in the breasts, and an increased need to pee have sex especially early in pregnancy less enjoyable. In general, these symptoms subside late in pregnancy and some women find that their libido increases. Some women also find that they are free from contraceptive concerns and that new intimacy with their partners enhances sex. As the uterus grows larger and the reality of what is to come begins, cravings subside again in the third trimester. Your partner’s libido may also increase or decrease. Some people even get closer to their pregnant partners and enjoy the changes in their bodies. Others may have reduced their desires by fearing the burden on their parents or by worrying about the health of both the mother and the fetus. Your partner may find it difficult to harmonize your identity as a sexual partner with your new (and increasingly visible) identity as a pregnant mother. Again, keep in mind that communicating with your partner can be very helpful in addressing these issues.
Sex after pregnancy:
After your doctor gives you a green light to resume sexual activity, you may still need to take things slowly. Remember: In addition to physical recovery, you are adapting to new family members, reducing sleep, and changing your daily life.
If you have a perineal tear or episiotomy, you may have to wait longer. An episiotomy is a surgical incision made to widen the vaginal canal. Returning to premature sex may increase the risk of complications such as postpartum bleeding.
You might always wonder how long delivery might affect you after having sex. Sex after delivery will feel different. One small study from 2005 found that 83 percent of females experienced sexual problems in the first three months after their first delivery. However, that number continues to fall as the post-pregnancy month’s increase.
The most common issues with sex after delivery include vaginal dryness, thin vaginal tissue, loss of elasticity in vaginal tissue, perineal tear or episiotomy, bleeding, pain, “loose” muscles, soreness, fatigue, low libido, etc. Hormones play a big role in post-delivery recovery and a return to normal sexual activity.
In the days immediately following childbirth, your estrogen drops to pre-pregnancy levels. If breastfeeding, estrogen levels might sink below pre-pregnancy levels. Estrogen helps supply natural vaginal lubrication, so low levels of the hormone increase the likelihood of vaginal dryness. Dry tissue can lead to irritation, even bleeding, during sex. This increases your risk of infection. Vaginal delivery can temporarily stretch the muscles of the vaginal canal. These muscles need time to regain their strength and stability. If a perineal tear or episiotomy is performed during vaginal delivery, recovery may take longer. If you have sex too early, you may be at increased risk of infection. Cesarean section can also impair vaginal sensation. The same hormonal issues can make the tissues of the vagina dry and thin, leading to painful sex. Plus, you`ll be recovering from abdominal surgery, so you`ll want to make sure the incision site has properly healed before resuming sex.
You might want to know how soon you can get pregnant after your delivery. You can get pregnant surprisingly quickly after delivering a baby. One study found the first ovulation for women who weren`t breastfeeding is around six weeks. Some women ovulated even earlier. If you are breastfeeding, the hormonal effects of breastfeeding serve as a “natural” contraceptive method for the first 4-6 months after delivery. Breastfeeding is 98% effective as a form of contraception for women, including less than 6 months after giving birth, those who are still breastfeeding their child and do not have their period yet. However, only about 1 in 4 females who use this method of lactational amenorrhea (LAM) or breastfeeding as a contraceptive do it correctly. This increases the risk of pregnancy. If you have sex after pregnancy but do not want to put another baby at risk right away, plan to use a reliable contraceptive method. A barrier method, such as a condom, maybe good to use at first. An implant or IUD can also be used. However, hormonal options may affect breastfeeding and can also come with certain risks, such as an increased risk for blood clots. Talk with your doctor about the right options for you.
When to contact your doctor
Pregnancy leads to a lot of physical changes in your body. That is why it is important to give yourself four to six weeks after delivery before you have sex again. During your recovery period, the uterus will shrink, hormones will return to pre-pregnancy levels, and muscles will regain strength and stability. After you`ve visited your doctor, be sure to take your time with returning to intercourse.
If you experience any pain or symptoms that persist, talk with your doctor. Painful sex can be a sign of other medical conditions that are not related to the recovery of pregnancy. If you are not sure whether sex is safe, contact your doctor. Also, call if you experience any unusual symptoms such as pain, bleeding, or secretions after sexual intercourse, or if you experience contractions that appear to stop after sexual intercourse. Remember that normal is a relative term when it comes to sex during pregnancy. You and your partner need to discuss what you feel is right for both you and yourself.