What are the Nutrients Found in Root Vegetables?
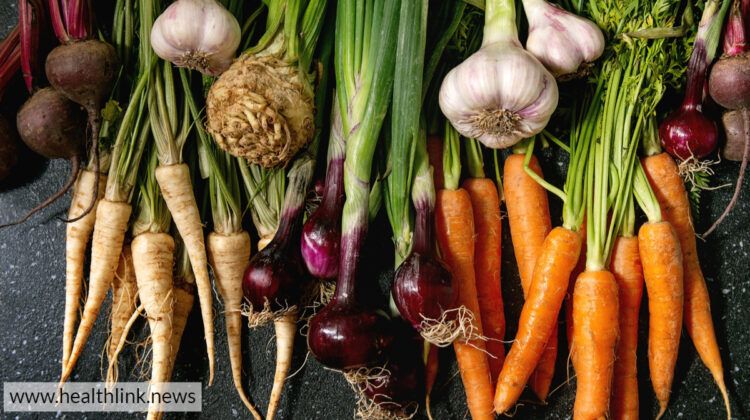

Root vegetables have long been enjoyed as a delicious part of a healthy diet! Although you’re most familiar with potatoes, carrots, and onions, many other types are also a part of the root vegetable family. Be sure to try some beetroot, parsnips, turnips, and celeriac — each with a distinct set of nutrients and health benefits.
Here is a shortlist of the health benefits you can reap from adding these root veggies to your regular rotation.
1. Potatoes
Potatoes are cultivated extensively all over the globe and fill a variety of different roles in food. Their nutritional value varies depending on the type of potato you choose, but they’re usually a good source of fiber, vitamin C, vitamin B6, and potassium.
Potatoes contain so much better than just starch. They’re a major source of vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, including vitamin C and manganese. Choose firm potatoes, with no signs of bruising or sprouting. Peeling your potatoes is optional depending on your recipe choice.
Good sources of potassium, potatoes can also help lower blood pressure and reduce the risk for developing diabetes as well as a threatening condition called metabolic syndrome.
2. Rutabaga
Root vegetables are very healthy additions to any diet, and rutabagas are no exception. Rutabagas are a root crop related to turnips, radishes, and horseradish and are commonly cultivated for their edible leaves and roots.
Rutabagas are root vegetables that are related to turnips and are a cross between a cabbage and a turnip. This source of fiber will help support your digestive health and lower blood pressure and cholesterol levels, while they also provide glucosinolates, sulfur-containing compounds that are commonly found in cruciferous vegetables that may help protect against cancer cell growth and development and prevent oxidative stress. Root Vegetables – Rutabaga can be mashed, baked, or roasted and enjoyed in soups, salads, noodles, and even desserts.
3. Radishes
Small in stature, these radishes pack a big nutritional punch. They’re low in calories and carbs yet high in fiber. These small, sweet, and spicy root vegetables are a nutrition powerhouse, containing more fiber than a baked potato. They’re also low in calories and carbs, making them an excellent choice for those following a low-carb diet.
The radish plant belongs to the mustard family, which includes other veggies like cabbage, kale, and cauliflower. Similar in appearance to a small turnip, it’s clear why they were nicknamed “honesty roots.” Radishes are crunchy and peppery by nature and can take on savory or sweet flavors just as easily.
4. Celeriac
A highly versatile and delicious root vegetable, the unassuming celeriac boasts a wonderful texture that is both creamy and crisp. Easy to cook and enjoyable to eat, it also contains a hearty dose of vitamin C and phosphorus, making it an excellent source of vitamin K (80% one cup). Whether roasted or mashed, steamed or stews, celeriac can be prepared in many different ways.
Celeriac, also known as celery root, is a root vegetable packed with nutrients. With an extremely high vitamin K content and an excellent source of vitamin C, this plant has been utilized for centuries for its health benefits. It can be eaten raw or cooked and is a delicious way to add a bit of variety to your daily diet.
5. Fennel
Low calorie, high fiber, and vitamin-packed; fennel is a great choice for weight watchers. This flavourful and nutritious veggie also boasts calcium, potassium, and manganese. Consume as part of a varied diet and healthy lifestyle.
Fennel is related to the carrot, celery, and parsley, and all of them contain a phytochemical called anethole, which has a wide array of health benefits. Fennel also has something called phytonutrients. Simply put, these are compounds that your body needs for things like coloring and protecting cells, making new tissue, and metabolizing food.
Fennel is a member of the carrot family, so it contains anti-inflammatory carotenoids. The bulb’s core, the brown or green part that surrounds the feathery fronds, can be eaten raw, or cooked and is sometimes pickled. Fennel can be enjoyed fresh, roasted, or sauteed, as well as mixed into salads, soups, sauces, and pasta dishes.
6. Carrots
Not only are carrots sweet and crunchy, but they’re also packed with nutrients like vitamins A, K, and C. In the world of root vegetables, their exceptional antioxidant content has made them a favorite among herbalists for centuries.
Eat more carrots to improve overall health. They are an excellent source of vitamin A and vitamin K, which may be associated with a lower risk of certain types of cancer, including breast, prostate, and stomach cancer. Beta-carotene and other carotenoids act as antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals that can damage cells and cause disease.
Carrots are a vegetable that is great for you and delicious, too! Carrots have so much fiber and nutrients, such as vitamin A and C, and some may help reduce the risk of cancer. Most importantly, carrots are sweet and delicious. You can eat them raw in salads or toasted with some hummus, or you can cook them in stir-fries, stews, or side dishes.
7. Turmeric
Turmeric is a type of root vegetable. Turmeric belongs to the ginger family, which also includes cardamom, galangal, and cassia bark. Turmeric has an orange tone with a spicy taste.
Turmeric root, a relative of ginger, is a powerful anti-inflammatory that has been used for centuries in both Eastern and Western medicine. It’s commonly consumed in curries and can be easily incorporated in drinks, such as golden turmeric milk.
Turmeric could be your new best friend for healthy, glowing skin and a well-performing brain. It contains the compound curcumin (along with many other beneficial substances) which can even help to beat the blues. Turmeric is a wonderfully versatile spice that adds color, warmth, and flavor to sweet and savory dishes – it’s an essential addition to any kitchen.
8. Ginger
Root Vegetables- Ginger. Root vegetables, or root crops, are grown from parts of plants that are below ground. They include many varieties of vegetables and other edible parts such as tuberous roots, bulbs, or rhizomes. Most root vegetables are high in fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
Ginger has a tangy, spicy flavor that is often used for hot dishes like stir-fries, curries, and stews. It is also used in sweets and drinks like tea, whiskey, and ginger ale. Ginger’s main health benefit comes from the chemical gingerol.
Ginger is a root vegetable that can be used in many dishes. The best way to preserve ginger is in either sugar syrup or vinegar. Ginger preserves very well because it has high sugar content.
9. Garlic
Garlic is a bulbous perennial that must be planted every several years. Each serving of garlic boasts a good amount of several important nutrients, including manganese and vitamin C. Try it in a variety of dishes, as it works well fried, baked, and delicious raw.
The bulb of the garlic plant consists of sections called cloves. Each clove is like a little onion with a wrapper made of skin that must be removed before eating. While many people eat garlic raw, it is generally cooked to bring out its full flavor and lessen its pungent taste. It’s also a good idea to use cooking methods that help preserve garlic’s nutrients.
If you’re looking to add a distinctive flavor to your meals and beverages, look no further than garlic. Its strong aroma, taste, and pungent smell repel bacteria and insects, making it an excellent source of prevention against the common cold. Best of all, garlic works well with a variety of foods, including soups and sauces.
10. Beets
Beets are delicious, flavourful, and nutritious! These red powerhouses offer a high concentration of folate, manganese, and nitrates. They’re also quite versatile. Roasted or sautéed they become sweet and tender. Enjoy them whole in cold salads or shredded in vibrant slaws.
So, what’s so great about beets? Beets are packed with antioxidants called betalains, which can help support healthy blood flow and boost your immune system, in addition to helping prevent cardiovascular disease.
11. Turnips
The turnip is a root vegetable that can trace its roots back to the 15th century. It has an impressive nutrient profile, being a great source of vitamin C, fiber, manganese, and potassium. One thing that’s likely to surprise most people is that it also has antifungal properties, making it a great remedy for preventing yeast infections.
Turnips are tasty and nutritious with a unique taste. They are a rich source of vitamins C, K, and A have B-complex and calcium. Turnips can be substituted into most recipes in place of potatoes. Plus, they’re easy to grow in your garden.
12. Onions
Onions are a very popular ingredient in many cuisines around the world and serve as a staple in most household pantries. High in fiber, vitamin C, and antioxidants, onions are linked with a wide array of health benefits.
Onions are a delicious root vegetable. Onions add flavor to a wide range of dishes, from appetizers to grilled meats. Try slicing onions into strips, or thin-slicing them for burgers and sandwiches. Roast whole onions until they become tender and use them as a topping on casseroles.
Loaded with flavor and low in fat, onions are a great addition to many meals. Onions may also help lower your risk of developing certain types of cancers since observational studies have linked a higher intake of these flavourful vegetables to a lower risk of common types of cancer.
13. Sweet Potatoes
A great source of fiber, vitamin C, manganese, and vitamin A and a good source of several antioxidants — including beta-carotene, chlorogenic acid, and anthocyanins. Sweet potatoes are highly nutritious root vegetables that are especially beneficial for immune health. Enjoy them steamed, roasted, or in soups or stews.
Sweet potatoes are loaded with carotenoids and antioxidant polyphenols that protect against diabetes. The orange flesh of sweet potatoes is color rich in beta-carotene, alpha-carotene, and vitamin A. Sweet potatoes also improve blood sugar control and provide 4 grams of white sweet potato extract per serving to help lower blood sugar.
Sweet potatoes are packed with nutrients and deliver a variety of health benefits. The vitamin A in sweet potatoes helps regulate healthy eyesight and may also help improve immune function and protect against other chronic diseases.